 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }Algoritam obrnutog brisanja usko je povezan s Kruskalov algoritam . U Kruskalovom algoritmu ono što radimo je: Sortirati rubove rastućim redoslijedom njihovih težina. Nakon sortiranja, jedan po jedan biramo rubove rastućim redoslijedom. Uključujemo trenutni odabrani brid ako uključivanjem ovoga u razapinjuće stablo ne formiramo nikakav ciklus sve dok ne bude V-1 bridova u razapinjućem stablu gdje je V = broj vrhova.
U algoritmu obrnutog brisanja sortiramo sve rubove smanjujući se redoslijed njihovih težina. Nakon sortiranja, jedan po jedan biramo rubove u silaznom redoslijedu. Mi uključi trenutni odabrani rub ako isključivanje trenutnog ruba uzrokuje prekid veze u trenutnom grafu . Glavna ideja je brisanje ruba ako njegovo brisanje ne dovodi do prekida veze grafa.
hiba bukhari
Algoritam:
- Razvrstaj sve rubove grafa u nerastućem redoslijedu težine rubova.
- Inicijalizirajte MST kao izvorni graf i uklonite dodatne bridove koristeći korak 3.
- Odaberite rub najveće težine od preostalih rubova i provjerite prekida li brisanje ruba graf ili ne .
Ako se prekine, ne brišemo rub.
Inače brišemo rub i nastavljamo.
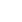
Ilustracija:
Razumimo na sljedećem primjeru:
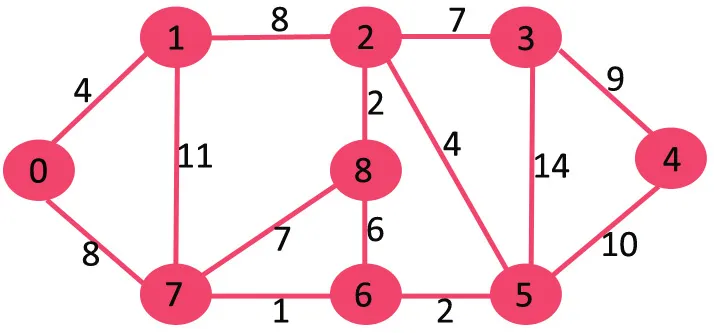
Ako izbrišemo najviši rub težine 14, graf se ne odvaja pa ga uklanjamo.
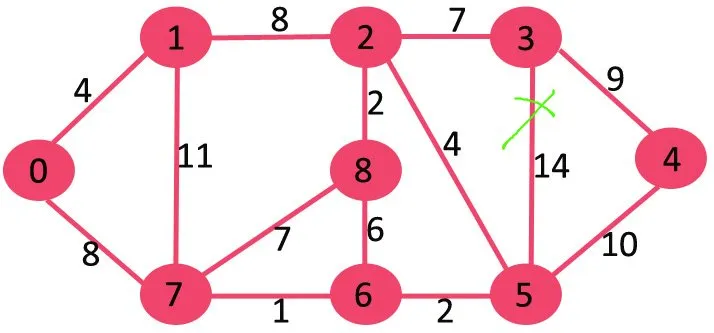
Zatim brišemo 11 jer njegovo brisanje ne odvaja graf.
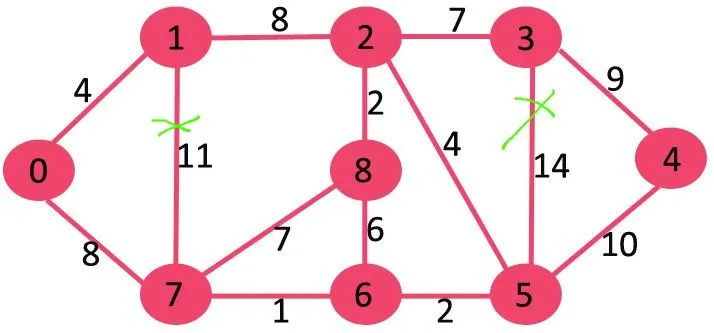
Zatim brišemo 10 jer njegovo brisanje ne odvaja graf.

Sljedeći je 9. Ne možemo izbrisati 9 jer njegovo brisanje uzrokuje prekid veze.
rukovanje nizovima u c++

Nastavljamo ovim putem i sljedeći rubovi ostaju u konačnom MST-u.
Edges in MST
(3 4)
(0 7)
(2 3)
(2 5)
(0 1)
(5 6)
(2 8)
(6 7)
Napomena: U slučaju rubova iste težine možemo odabrati bilo koji rub rubova iste težine.
Preporučena praksa Algoritam obrnutog brisanja za minimalno razapinjuće stablo Probajte!Implementacija:
C++// C++ program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm #include
// Java program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm import java.util.*; // class to represent an edge class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> { int u v w; Edge(int u int v int w) { this.u = u; this.w = w; this.v = v; } public int compareTo(Edge other) { return (this.w - other.w); } } // Class to represent a graph using adjacency list // representation public class GFG { private int V; // No. of vertices private List<Integer>[] adj; private List<Edge> edges; @SuppressWarnings({ 'unchecked' 'deprecated' }) public GFG(int v) // Constructor { V = v; adj = new ArrayList[v]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) adj[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>(); edges = new ArrayList<Edge>(); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge(int u int v int w) { adj[u].add(v); // Add w to v’s list. adj[v].add(u); // Add w to v’s list. edges.add(new Edge(u v w)); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS(int v boolean[] visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex for (int i : adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) DFS(i visited); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private boolean IsConnected() { boolean[] visited = new boolean[V]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) return false; } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost Collections.sort(edges); int mst_wt = 0; // Initialize weight of MST System.out.println('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (int i = edges.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int u = edges.get(i).u; int v = edges.get(i).v; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj[u].remove(adj[u].indexOf(v)); adj[v].remove(adj[v].indexOf(u)); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (IsConnected() == false) { adj[u].add(v); adj[v].add(u); // This edge is part of MST System.out.println('(' + u + ' ' + v + ')'); mst_wt += edges.get(i).w; } } System.out.println('Total weight of MST is ' + mst_wt); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9; GFG g = new GFG(V); // making above shown graph g.AddEdge(0 1 4); g.AddEdge(0 7 8); g.AddEdge(1 2 8); g.AddEdge(1 7 11); g.AddEdge(2 3 7); g.AddEdge(2 8 2); g.AddEdge(2 5 4); g.AddEdge(3 4 9); g.AddEdge(3 5 14); g.AddEdge(4 5 10); g.AddEdge(5 6 2); g.AddEdge(6 7 1); g.AddEdge(6 8 6); g.AddEdge(7 8 7); g.ReverseDeleteMST(); } } // This code is contributed by Prithi_Dey
# Python3 program to find Minimum Spanning Tree # of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm # Graph class represents a directed graph # using adjacency list representation class Graph: def __init__(self v): # No. of vertices self.v = v self.adj = [0] * v self.edges = [] for i in range(v): self.adj[i] = [] # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge(self u: int v: int w: int): self.adj[u].append(v) # Add w to v’s list. self.adj[v].append(u) # Add w to v’s list. self.edges.append((w (u v))) def dfs(self v: int visited: list): # Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = True # Recur for all the vertices adjacent to # this vertex for i in self.adj[v]: if not visited[i]: self.dfs(i visited) # Returns true if graph is connected # Returns true if given graph is connected else false def connected(self): visited = [False] * self.v # Find all reachable vertices from first vertex self.dfs(0 visited) # If set of reachable vertices includes all # return true. for i in range(1 self.v): if not visited[i]: return False return True # This function assumes that edge (u v) # exists in graph or not def reverseDeleteMST(self): # Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost self.edges.sort(key = lambda a: a[0]) mst_wt = 0 # Initialize weight of MST print('Edges in MST') # Iterate through all sorted edges in # decreasing order of weights for i in range(len(self.edges) - 1 -1 -1): u = self.edges[i][1][0] v = self.edges[i][1][1] # Remove edge from undirected graph self.adj[u].remove(v) self.adj[v].remove(u) # Adding the edge back if removing it # causes disconnection. In this case this # edge becomes part of MST. if self.connected() == False: self.adj[u].append(v) self.adj[v].append(u) # This edge is part of MST print('( %d %d )' % (u v)) mst_wt += self.edges[i][0] print('Total weight of MST is' mst_wt) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # create the graph given in above figure V = 9 g = Graph(V) # making above shown graph g.addEdge(0 1 4) g.addEdge(0 7 8) g.addEdge(1 2 8) g.addEdge(1 7 11) g.addEdge(2 3 7) g.addEdge(2 8 2) g.addEdge(2 5 4) g.addEdge(3 4 9) g.addEdge(3 5 14) g.addEdge(4 5 10) g.addEdge(5 6 2) g.addEdge(6 7 1) g.addEdge(6 8 6) g.addEdge(7 8 7) g.reverseDeleteMST() # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552
// C# program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // class to represent an edge public class Edge : IComparable<Edge> { public int u v w; public Edge(int u int v int w) { this.u = u; this.v = v; this.w = w; } public int CompareTo(Edge other) { return this.w.CompareTo(other.w); } } // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation public class Graph { private int V; // No. of vertices private List<int>[] adj; private List<Edge> edges; public Graph(int v) // Constructor { V = v; adj = new List<int>[ v ]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) adj[i] = new List<int>(); edges = new List<Edge>(); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge(int u int v int w) { adj[u].Add(v); // Add w to v’s list. adj[v].Add(u); // Add w to v’s list. edges.Add(new Edge(u v w)); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS(int v bool[] visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex foreach(int i in adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) DFS(i visited); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private bool IsConnected() { bool[] visited = new bool[V]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) return false; } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost edges.Sort(); int mst_wt = 0; // Initialize weight of MST Console.WriteLine('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (int i = edges.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int u = edges[i].u; int v = edges[i].v; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj[u].Remove(v); adj[v].Remove(u); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (IsConnected() == false) { adj[u].Add(v); adj[v].Add(u); // This edge is part of MST Console.WriteLine('({0} {1})' u v); mst_wt += edges[i].w; } } Console.WriteLine('Total weight of MST is {0}' mst_wt); } } class GFG { // Driver code static void Main(string[] args) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9; Graph g = new Graph(V); // making above shown graph g.AddEdge(0 1 4); g.AddEdge(0 7 8); g.AddEdge(1 2 8); g.AddEdge(1 7 11); g.AddEdge(2 3 7); g.AddEdge(2 8 2); g.AddEdge(2 5 4); g.AddEdge(3 4 9); g.AddEdge(3 5 14); g.AddEdge(4 5 10); g.AddEdge(5 6 2); g.AddEdge(6 7 1); g.AddEdge(6 8 6); g.AddEdge(7 8 7); g.ReverseDeleteMST(); } } // This code is contributed by cavi4762
// Javascript program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation class Graph { // Constructor constructor(V) { this.V = V; this.adj = []; this.edges = []; for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) { this.adj[i] = []; } } // function to add an edge to graph addEdge(u v w) { this.adj[u].push(v);// Add w to v’s list. this.adj[v].push(u);// Add w to v’s list. this.edges.push([w [u v]]); } DFS(v visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; for (const i of this.adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) { this.DFS(i visited); } } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false isConnected() { const visited = []; for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++) { visited[i] = false; } // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex this.DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (let i = 1; i < this.V; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { return false; } } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not reverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost this.edges.sort((a b) => a[0] - b[0]); let mstWt = 0;// Initialize weight of MST console.log('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (let i = this.edges.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { const [u v] = this.edges[i][1]; // Remove edge from undirected graph this.adj[u] = this.adj[u].filter(x => x !== v); this.adj[v] = this.adj[v].filter(x => x !== u); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (!this.isConnected()) { this.adj[u].push(v); this.adj[v].push(u); // This edge is part of MST console.log(`(${u} ${v})`); mstWt += this.edges[i][0]; } } console.log(`Total weight of MST is ${mstWt}`); } } // Driver code function main() { // create the graph given in above figure var V = 9; var g = new Graph(V); // making above shown graph g.addEdge(0 1 4); g.addEdge(0 7 8); g.addEdge(1 2 8); g.addEdge(1 7 11); g.addEdge(2 3 7); g.addEdge(2 8 2); g.addEdge(2 5 4); g.addEdge(3 4 9); g.addEdge(3 5 14); g.addEdge(4 5 10); g.addEdge(5 6 2); g.addEdge(6 7 1); g.addEdge(6 8 6); g.addEdge(7 8 7); g.reverseDeleteMST(); } main();
Izlaz
Edges in MST (3 4) (0 7) (2 3) (2 5) (0 1) (5 6) (2 8) (6 7) Total weight of MST is 37
Vremenska složenost: O((E*(V+E)) + E log E) gdje je E broj bridova.
Složenost prostora: O(V+E) gdje je V broj vrhova, a E broj bridova. Koristimo popis susjedstva za pohranjivanje grafa pa nam treba prostor proporcionalan O(V+E).
Bilješke:
- Gore navedena implementacija je jednostavna/naivna implementacija algoritma obrnutog brisanja i može se optimizirati na O(E log V (log log V)3) [Izvor: Tjedan dana ]. Ali ova optimizirana vremenska složenost još uvijek je manja od Prim i Kruškal Algoritmi za MST.
- Gornja implementacija modificira izvorni grafikon. Možemo izraditi kopiju grafa ako se izvorni graf mora zadržati.
Napravi kviz
