 #practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }
#practiceLinkDiv { display: none !important; }Zadan je skup točaka kao i pravac kao ax+by+c = 0. Moramo pronaći točku na zadanom pravcu za koji je zbroj udaljenosti od zadanog skupa točaka minimalan.
Primjer:
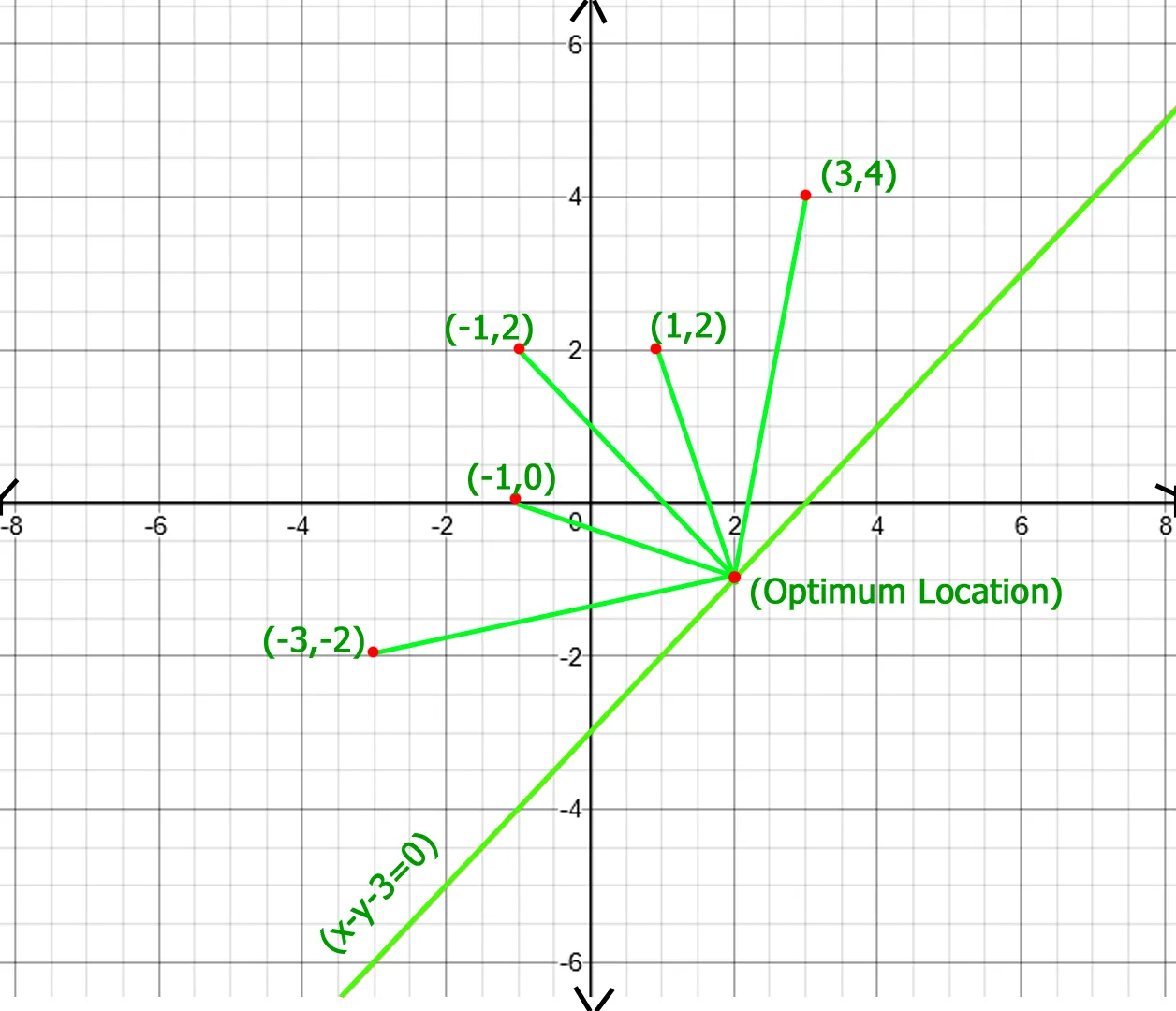
In above figure optimum location of point of x - y - 3 = 0 line is (2 -1) whose total distance with other points is 20.77 which is minimum obtainable total distance.Recommended Practice Optimalna lokacija točke za smanjenje ukupne udaljenosti Probajte!
Ako uzmemo jednu točku na danoj liniji na beskonačnoj udaljenosti tada će ukupni trošak udaljenosti biti beskonačan sada kada pomičemo ovu točku na liniji prema danim točkama, ukupni trošak udaljenosti počinje se smanjivati i nakon nekog vremena ponovno počinje rasti što je doseglo beskonačnost na drugom beskonačnom kraju crte tako da krivulja troška udaljenosti izgleda kao U-krivulja i moramo pronaći donju vrijednost te U-krivulje.
Budući da U-krivulja nije monotono rastuća ili opadajuća, ne možemo koristiti binarno pretraživanje za pronalaženje najniže točke ovdje ćemo koristiti trojno pretraživanje za pronalaženje najdonje točke ternarno pretraživanje preskače jednu trećinu prostora za pretraživanje pri svakoj iteraciji, možete pročitati više o ternarnom pretraživanju ovdje .
Dakle, rješenje se nastavlja na sljedeći način, počinjemo s niskim i visokim inicijaliziranim kao neke najmanje i najveće vrijednosti, zatim započinjemo iteraciju u svakoj iteraciji, izračunavamo dvije sredine mid1 i mid2 koje predstavljaju 1/3. i 2/3. poziciju u prostoru pretraživanja, izračunavamo ukupnu udaljenost svih točaka sa mid1 i mid2 i ažuriramo nisku ili visoku usporedbom tih troškova udaljenosti. Ova iteracija se nastavlja dok niska i visoka ne postanu približno jednake.
C++// C/C++ program to find optimum location and total cost #include
// A Java program to find optimum location // and total cost class GFG { static double sq(double x) { return ((x) * (x)); } static int EPS = (int)(1e-6) + 1; static int N = 5; // structure defining a point static class point { int x y; point() {} public point(int x int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } }; // structure defining a line of ax + by + c = 0 form static class line { int a b c; public line(int a int b int c) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } }; // method to get distance of point (x y) from point p static double dist(double x double y point p) { return Math.sqrt(sq(x - p.x) + sq(y - p.y)); } /* Utility method to compute total distance all points when choose point on given line has x-coordinate value as X */ static double compute(point p[] int n line l double X) { double res = 0; // calculating Y of chosen point by line equation double Y = -1 * (l.c + l.a * X) / l.b; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) res += dist(X Y p[i]); return res; } // Utility method to find minimum total distance static double findOptimumCostUtil(point p[] int n line l) { double low = -1e6; double high = 1e6; // loop until difference between low and high // become less than EPS while ((high - low) > EPS) { // mid1 and mid2 are representative x // co-ordiantes of search space double mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3; double mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3; double dist1 = compute(p n l mid1); double dist2 = compute(p n l mid2); // if mid2 point gives more total distance // skip third part if (dist1 < dist2) high = mid2; // if mid1 point gives more total distance // skip first part else low = mid1; } // compute optimum distance cost by sending average // of low and high as X return compute(p n l (low + high) / 2); } // method to find optimum cost static double findOptimumCost(int points[][] line l) { point[] p = new point[N]; // converting 2D array input to point array for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i] = new point(points[i][0] points[i][1]); return findOptimumCostUtil(p N l); } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { line l = new line(1 -1 -3); int points[][] = { { -3 -2 } { -1 0 } { -1 2 } { 1 2 } { 3 4 } }; System.out.println(findOptimumCost(points l)); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
# A Python3 program to find optimum location # and total cost import math class Optimum_distance: # Class defining a point class Point: def __init__(self x y): self.x = x self.y = y # Class defining a line of ax + by + c = 0 form class Line: def __init__(self a b c): self.a = a self.b = b self.c = c # Method to get distance of point # (x y) from point p def dist(self x y p): return math.sqrt((x - p.x) ** 2 + (y - p.y) ** 2) # Utility method to compute total distance # all points when choose point on given # line has x-coordinate value as X def compute(self p n l x): res = 0 y = -1 * (l.a*x + l.c) / l.b # Calculating Y of chosen point # by line equation for i in range(n): res += self.dist(x y p[i]) return res # Utility method to find minimum total distance def find_Optimum_cost_untill(self p n l): low = -1e6 high = 1e6 eps = 1e-6 + 1 # Loop until difference between low # and high become less than EPS while((high - low) > eps): # mid1 and mid2 are representative x # co-ordiantes of search space mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3 mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3 dist1 = self.compute(p n l mid1) dist2 = self.compute(p n l mid2) # If mid2 point gives more total # distance skip third part if (dist1 < dist2): high = mid2 # If mid1 point gives more total # distance skip first part else: low = mid1 # Compute optimum distance cost by # sending average of low and high as X return self.compute(p n l (low + high) / 2) # Method to find optimum cost def find_Optimum_cost(self p l): n = len(p) p_arr = [None] * n # Converting 2D array input to point array for i in range(n): p_obj = self.Point(p[i][0] p[i][1]) p_arr[i] = p_obj return self.find_Optimum_cost_untill(p_arr n l) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': obj = Optimum_distance() l = obj.Line(1 -1 -3) p = [ [ -3 -2 ] [ -1 0 ] [ -1 2 ] [ 1 2 ] [ 3 4 ] ] print(obj.find_Optimum_cost(p l)) # This code is contributed by Sulu_mufi
// C# program to find optimum location // and total cost using System; class GFG { static double sq(double x) { return ((x) * (x)); } static int EPS = (int)(1e-6) + 1; static int N = 5; // structure defining a point public class point { public int x y; public point() {} public point(int x int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } }; // structure defining a line // of ax + by + c = 0 form public class line { public int a b c; public line(int a int b int c) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } }; // method to get distance of // point (x y) from point p static double dist(double x double y point p) { return Math.Sqrt(sq(x - p.x) + sq(y - p.y)); } /* Utility method to compute total distance of all points when choose point on given line has x-coordinate value as X */ static double compute(point[] p int n line l double X) { double res = 0; // calculating Y of chosen point // by line equation double Y = -1 * (l.c + l.a * X) / l.b; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) res += dist(X Y p[i]); return res; } // Utility method to find minimum total distance static double findOptimumCostUtil(point[] p int n line l) { double low = -1e6; double high = 1e6; // loop until difference between // low and high become less than EPS while ((high - low) > EPS) { // mid1 and mid2 are representative // x co-ordiantes of search space double mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3; double mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3; double dist1 = compute(p n l mid1); double dist2 = compute(p n l mid2); // if mid2 point gives more total distance // skip third part if (dist1 < dist2) high = mid2; // if mid1 point gives more total distance // skip first part else low = mid1; } // compute optimum distance cost by // sending average of low and high as X return compute(p n l (low + high) / 2); } // method to find optimum cost static double findOptimumCost(int[ ] points line l) { point[] p = new point[N]; // converting 2D array input to point array for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i] = new point(points[i 0] points[i 1]); return findOptimumCostUtil(p N l); } // Driver Code public static void Main(String[] args) { line l = new line(1 -1 -3); int[ ] points = { { -3 -2 } { -1 0 } { -1 2 } { 1 2 } { 3 4 } }; Console.WriteLine(findOptimumCost(points l)); } } // This code is contributed by 29AjayKumar
<script> // A JavaScript program to find optimum location // and total cost function sq(x) { return x*x; } let EPS = (1e-6) + 1; let N = 5; // structure defining a point class point { constructor(xy) { this.x=x; this.y=y; } } // structure defining a line of ax + by + c = 0 form class line { constructor(abc) { this.a = a; this.b = b; this.c = c; } } // method to get distance of point (x y) from point p function dist(xyp) { return Math.sqrt(sq(x - p.x) + sq(y - p.y)); } /* Utility method to compute total distance all points when choose point on given line has x-coordinate value as X */ function compute(pnlX) { let res = 0; // calculating Y of chosen point by line equation let Y = -1 * (l.c + l.a * X) / l.b; for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) res += dist(X Y p[i]); return res; } // Utility method to find minimum total distance function findOptimumCostUtil(pnl) { let low = -1e6; let high = 1e6; // loop until difference between low and high // become less than EPS while ((high - low) > EPS) { // mid1 and mid2 are representative x // co-ordiantes of search space let mid1 = low + (high - low) / 3; let mid2 = high - (high - low) / 3; let dist1 = compute(p n l mid1); let dist2 = compute(p n l mid2); // if mid2 point gives more total distance // skip third part if (dist1 < dist2) high = mid2; // if mid1 point gives more total distance // skip first part else low = mid1; } // compute optimum distance cost by sending average // of low and high as X return compute(p n l (low + high) / 2); } // method to find optimum cost function findOptimumCost(pointsl) { let p = new Array(N); // converting 2D array input to point array for (let i = 0; i < N; i++) p[i] = new point(points[i][0] points[i][1]); return findOptimumCostUtil(p N l); } // Driver Code let l = new line(1 -1 -3); let points= [[ -3 -2 ] [ -1 0 ] [ -1 2 ] [ 1 2 ] [ 3 4 ]]; document.write(findOptimumCost(points l)); // This code is contributed by rag2127 </script>
Izlaz
20.7652
Vremenska složenost: Na2)
Pomoćni prostor: Na)
